Der Bullwhip-Effekt ist ein bekanntes Problem in Lieferketten. Selbst kleine Nachfrageschwankungen auf Verbraucherebene können große, unkontrollierbare Ausschläge entlang der gesamten Lieferkette verursachen. Dies führt zu ineffizienten Prozessen, Überproduktion und hohen Lagerbeständen. KI kann den Bullwhip-Effekt glätten, indem sie präzisere Bedarfsprognosen ermöglicht, Verzögerungen im Informationsfluss reduziert und die Zusammenarbeit zwischen Lieferkettenpartnern optimiert. Unternehmen, die KI zur Glättung des Bullwhip-Effekts einsetzen, profitieren von stabileren Prozessen und einer besseren Marktanpassung.
Herausforderungen durch den Bullwhip-Effekt und Lösungen durch KI
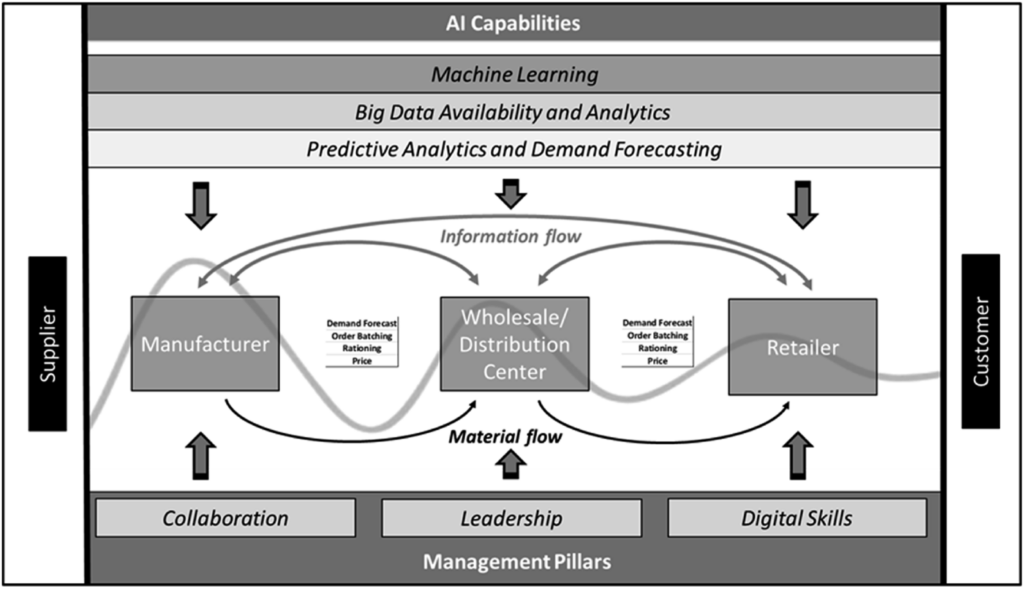
Laut der Studie kann KI den Bullwhip-Effekt abmildern, indem sie zentrale Managementfaktoren wie Zusammenarbeit, Führung und digitale Fertigkeiten verbessert. Diese Aspekte sind entscheidend für die erfolgreiche Integration von KI in Lieferketten und tragen maßgeblich zur Reduzierung von Nachfrageschwankungen bei.
Die Rolle der KI im Lieferkettenmanagement zur Reduzierung des Bullwhip-Effekts
Laut den Autoren kann KI den Bullwhip-Effekt abmildern. Dies geschieht, indem sie wichtige Managementpfeiler wie Zusammenarbeit, Führung und digitale Fähigkeiten verbessert. Diese Säulen sind somit für die erfolgreiche Integration von KI in Lieferketten entscheidend.
1. Zusammenarbeit:
KI verbessert die Kommunikation und den Datenaustausch zwischen Herstellern, Großhändlern und Einzelhändlern. Durch den Einsatz von KI können Unternehmen Daten in Echtzeit austauschen und so Verzögerungen vermeiden. Dies führt zu genaueren Bedarfsprognosen, was wiederum hilft, den Bullwhip-Effekt mit KI-Technologien zu glätten.
Die Studie weist jedoch darauf hin, dass die Rolle von KI beim Aufbau von Vertrauen in Lieferketten bislang nur begrenzt erforscht wurde. Vertrauen ist jedoch ein entscheidendes Element für jede effektive Zusammenarbeit. Künftige Forschungen sollten sich daher darauf konzentrieren, wie KI dazu beitragen kann, vertrauensbezogene Herausforderungen in Lieferketten zu bewältigen.
2. Führung:
Eine starke Führung ist für die erfolgreiche Einführung von KI in Lieferketten unerlässlich. Die Studie unterstreicht, dass Führungskräfte sich nicht nur auf die technischen Aspekte der KI-Integration konzentrieren dürfen. Vielmehr müssen sie auch die menschlichen Dimensionen beherrschen – insbesondere das Veränderungsmanagement und die Steuerung der organisatorischen Dynamik.
Führungskräfte müssen sich darauf einstellen, dass die Einführung von KI nicht nur einen technologischen, sondern auch einen kulturellen Wandel in Unternehmen mit sich bringt. Unternehmen, die den Wandel aktiv managen, können KI nutzen, um den Bullwhip-Effekt in Lieferketten zu reduzieren.
3. Digitale Fertigkeiten:
Damit KI den Bullwhip-Effekt in der Lieferkette effektiv glättet, müssen Unternehmen in den Aufbau einer digital qualifizierten Belegschaft investieren. Weisz, Herold und Kummer weisen auf die wachsende digitale Qualifikationslücke hin. Sie argumentieren daher, dass Unternehmen der Weiterbildung ihrer Mitarbeiter Vorrang einräumen müssen.
Nur durch eine digital kompetente Belegschaft kann KI effektiv eingesetzt werden, um den Informationsfluss zu optimieren und Bedarfsprognosen zu verbessern. Unternehmen, die frühzeitig in digitale Kompetenzen investieren, sind besser darauf vorbereitet, von den Vorteilen der KI zu profitieren und den Bullwhip-Effekt mit KI-gestützten Lösungen zu minimieren.
Wichtige Forschungslücken zur KI-gestützten Glättung des Bullwhip-Effekts
Die Studie weist auf mehrere Forschungslücken hin, die weiter untersucht werden müssen:
1. Die Rolle der KI bei der Bewältigung des Bullwhip-Effekts: Während den technischen Anwendungen der KI große Aufmerksamkeit gewidmet wurde, wurde ihrer Rolle bei der Glättung des Bullwhip-Effekts aus der Managementperspektive weniger Aufmerksamkeit geschenkt. Die Autoren schlagen daher vor, dass Rahmenwerke wie das von ihnen vorgeschlagene Bullwhip Smoothing Framework (BSF) eine Grundlage für zukünftige Studien bilden könnten.
2. Vertrauen und Zusammenarbeit in KI-gestützten Lieferketten: Obwohl die Zusammenarbeit ein Schlüsselfaktor für die Verringerung des Bullwhip-Effekts ist, gibt es nur wenige Untersuchungen, die KI mit kollaborativen Praktiken in Verbindung bringen. Es sind daher weitere Studien erforderlich, um zu untersuchen, wie KI Vertrauen aufbauen und Interessenkonflikte zwischen den Mitgliedern der Lieferkette bewältigen kann.
3. Führungsqualitäten und digitale Fähigkeiten für die KI-Integration: Die Studie stellt fest, dass es an detaillierter Forschung zu den spezifischen Führungsqualitäten und digitalen Fähigkeiten mangelt, die für eine erfolgreiche Implementierung von KI in Lieferketten erforderlich sind. Künftige Arbeiten sollten folglich die strukturellen Veränderungen und Qualifikationsanforderungen untersuchen, die für diesen Übergang erforderlich sind.
Theoretische und praktische Beiträge zur KI-Integration in Lieferketten
1. Theoretische Implikationen: Die Studie leistet einen wichtigen Beitrag, indem sie die Theorien des Lieferkettenmanagements um die Rolle der KI bei der Bekämpfung des Bullwhip-Effekts erweitert. Die Autoren schlagen das BSF als Instrument vor, um zu analysieren, wie KI das Bullwhip-Phänomen glätten kann. Sie konzentrieren sich dabei auf Zusammenarbeit, Führung und digitale Fähigkeiten.
2. Praktische Implikationen: Aus praktischer Sicht betonen die Autoren, dass die Einführung von KI allein nicht ausreicht, um den Bullwhip-Effekt zu beseitigen. Sie muss durch starke Managementpraktiken unterstützt werden. Führungskräfte müssen zudem transparente, ethische Rahmenbedingungen für den Einsatz von KI entwickeln. Gleichzeitig müssen sie sicherstellen, dass die Leistungskennzahlen der KI mit den Unternehmenszielen übereinstimmen.
Ein Aufruf zur weiteren Erforschung der KI im Kampf gegen den Bullwhip-Effekt
Die Studie von Weisz, Herold und Kummer ist ein wichtiger erster Schritt, um zu verstehen, wie KI den Bullwhip-Effekt in Lieferketten abschwächen kann. Wie die Autoren jedoch selbst betonen, befindet sich die Integration von KI in das Lieferkettenmanagement noch in einem frühen Stadium. Es gibt daher viele Möglichkeiten für weitere Forschung, insbesondere in den Bereichen KI-gesteuerte Zusammenarbeit, Führung und Entwicklung digitaler Fähigkeiten.
Da sich die KI weiterentwickelt und immer stärker in die Lieferketten integriert wird, sind Unternehmen, die diese drei Schlüsselsäulen effektiv verwalten können, am besten positioniert, um Ineffizienzen zu reduzieren und auf Marktanforderungen zu reagieren. Wir bei Circlly haben es uns daher zur Aufgabe gemacht, an der Spitze dieser technologischen Fortschritte zu bleiben und Einblicke zu bieten, wie sich Unternehmen an die Zukunft des Lieferkettenmanagements anpassen können.
For a deeper dive into the original research, you can check out the full study “Revisiting the Bullwhip Effect: How Can AI Smoothen the Bullwhip Phenomenon?” by Eric Weisz, David M. Herold and Sebastian Kummer.
Would you like to learn more about the optimization of your supply chain?
Contact us and arrange a personalised and non-binding consultation with our management.