Bedarfsprognosenmethode Maschinelles Lernen Predictive Analytics ist der Schlüssel zur Optimierung der Nachfrageplanung in einem sich schnell verändernden Markt. Unternehmen müssen auf diese Technologien setzen, da traditionelle Methoden oft nicht ausreichen, um plötzliche Veränderungen im Kaufverhalten der Verbraucher zu erfassen – sei es durch Wetterbedingungen, Social-Media-Trends oder globale Ereignisse. Laut dem IT-Forschungsunternehmen Gartner gehört die Nachfragevolatilität zu den größten Herausforderungen für Führungskräfte, weshalb präzise Prognosen wichtiger denn je sind.
Bedarfsprognosenmethode Maschinelles Lernen Predictive Analytics ermöglicht es Unternehmen, riesige Mengen an historischen und aktuellen Daten zu analysieren und genauere Nachfrageprognosen zu erstellen. Diese Technologien helfen dabei, Bestände zu optimieren, Marktveränderungen frühzeitig zu erkennen und fundierte Geschäftsentscheidungen zu treffen. In diesem Artikel zeigen wir, wie Bedarfsprognosenmethode Maschinelles Lernen Predictive Analytics die Nachfrageplanung revolutioniert und vergleichen traditionelle statistische Modelle mit modernen, KI-gestützten Ansätzen.
Der Stellenwert von Bedarfsprognosenmethode Maschinelles Lernen Predictive Analytics in der Angebotsplanung
Wie Bedarfsprognosenmethode Maschinelles Lernen Predictive Analytics die Effizienz steigert: Grundlagen und Methoden
Demand forecasting is the process of estimating the likely future demand for a product or service. The phrase is often used used interchangeably with demand planning, but the latter is a more broad process that begins with, but is not limited to, forecasting.
According to the Institute of Business Forecasting and Planning (IBF), demand planning "uses forecasts and experience to estimate demand for various items at different points in the supply chain." In addition to estimates, demand planners participate in inventory optimization, ensuring the availability of needed products and monitoring the gap between forecasts and actual sales.
Demand planning is the launch pad for many other activities, such as warehousing, distribution, price forecasting, and especially supply planning, which aims to meet demand and requires data on what customers are likely to want.
Here we return to forecasting. Being as close to reality as possible is key to improving efficiency throughout the supply chain. But how do you achieve the highest possible accuracy? The answer depends on the type of company, the available resources and the objectives.
So let's compare the available options: traditional statistical forecasting, machine learning algorithms, predictive analytics that combines both approaches, and demand sensing as a supporting tool.
Traditionelle statistische Prognosen vs. Bedarfsprognosenmethode Maschinelles Lernen Predictive Analytics
Traditional statistical methods (TSM) have been around for a long time and are still an integral part of forecasting processes in production and retail.
The only difference to earlier calculations is that they are now performed automatically by software solutions. For example, time series forecasts for sales and trends can be created in Excel.
To forecast the future, statistics uses data from the past. This is why statistical forecasts are often referred to as "historical analysis." Traditional forecasts are still the most popular method of predicting sales. Typically, demand planning solutions based on statistical techniques can be executed in Excel and existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems seamlessly, without the need for additional technical expertise. The most advanced systems may consider seasonality and market trends, as well as apply numerous methods to fine-tune results.
It should be noted that an important requirement for statistical forecast accuracy is the stability of the market. The analysis assumes that history repeats itself: situations that occurred two or three years ago will repeat themselves.
Demand patterns that can be measured well statistically:
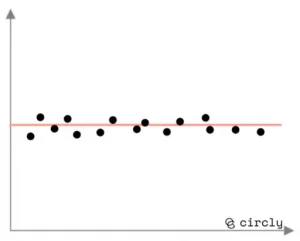
Constant demand curve
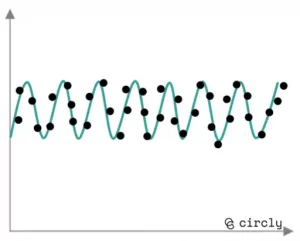
Seasonal demand pattern
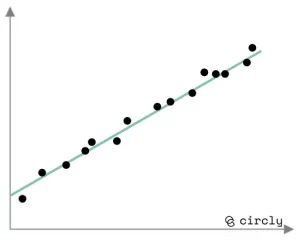
Trendy demand pattern
However, this is far from the reality. Statistical methods fail to predict illogical changes in customer preferences or to predict when market saturation will happen.
In summary, automated statistical forecasting provides a sufficient level of accuracy for:
1. Medium to long-term planning,
2. well-established products that have a stable demand, and
3. forecast of total demand
4. new product launches.
| Traditional Forecasts | Machine Learning Forecasts | Circly's AI Forcast | |
|---|---|---|---|
| How many variables and data sources can be factored in? | Adding additional variables and sources requires significant effort. | Multiple variables & sources can be easily integrated thanks to the high level of automation. | A variety of variables and provided data can be easily integrated. |
| Extent of manual work: | High | Low | Low |
| Amount of data required: | Low | Large | Medium to Large |
| Maintenance effort: | Low | High | Low |
| Technology requirements: | Low | High | Low to Medium |
| Best fit: | Long term planning Established products Stable demand |
Medium term planning New products Volatile demand scenarios |
Medium & short term planning Changing factors Existing processes |
Do you have questions about possible areas of use?
Haben Sie Fragen zur Umsetzung in Ihrem Unternehmen? Contact us für eine unverbindliche Beratung!
Further sources: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10590108
4. not suitable for sales planning of individual stock-keeping units (SKUs).
